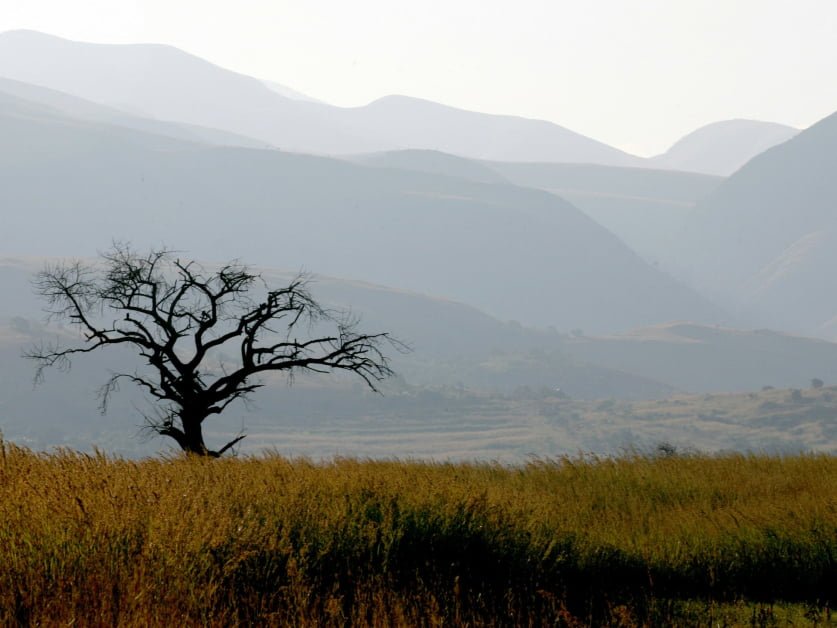
In the heart of the Jilobi Forest, located in the Lubombo region of Eswatini, three chiefdoms have put aside their longstanding disputes to come together in support of preserving their indigenous wooded area. This collaboration signifies a major milestone for the local communities, as they strive to protect their cultural heritage and natural resources for future generations. This article will explore the unique challenges faced by these chiefdoms, the journey towards reconciliation, and the innovative strategies being employed to ensure the sustainability of this precious wooded field. Let’s delve into how these three chiefdoms are setting an example in sustainable land management and conservation efforts in Eswatini.
Overcoming Rivalries for Conservation
The chiefdoms of Maphungwane, Tikhuba, and Lukhetseni in Eswatini had a history of disputes over boundary lines and resource management that led to strained relationships and hindered peaceful coexistence. These rivalries posed a serious threat to the biodiversity of the Jilobi Forest, resulting in illegal activities such as wood-cutting and cattle theft. The tensions attracted outsiders who exploited the situation, causing further harm to the forest’s resources.
Cultural Significance and Sustainable Practices
The Jilobi Forest holds cultural significance for the Maziya and Dlamini clans, with locals believing that the souls of their ancestors reside in the forest. Unsustainable practices like medicinal plant harvesting and poaching were endangering this natural treasure. However, the communities have a deep-rooted connection with the forest, relying on sustainable farming practices and responsible resource management to ensure its preservation.
Threats to a Biodiversity Hotspot
Deforestation and unchecked harvesting of resources in the Jilobi Forest posed a significant threat to its rich biodiversity. The rapid depletion of the forest’s resources by external communities and poachers endangered various plant and animal species. It became crucial for the chiefdoms to reconcile their differences and work together to protect and conserve the forest.
Collaborative Conservation Efforts
In a joint effort to preserve the Jilobi Forest, local and international organizations intervened, initiating an ecotourism development project aimed at sustainable forest management and reconciliation among the chiefdoms. The establishment of the Joint Management Committee facilitated the development of a reforestation plan and responsible forestry practices. Workshops were conducted to raise awareness about biodiversity and the forest’s role in mitigating climate change.
Positive Impacts and Concerns
The conservation initiatives have yielded positive results, with reduced illegal activities and improved community engagement in forest preservation. However, there are concerns about the intentions of external organizations promoting conservation efforts, with some community members questioning their motivations. Despite differing opinions, the collaborative efforts have brought about a positive shift in community attitudes towards conservation.
Conclusion
The journey towards conservation and reconciliation in the Jilobi Forest represents a significant turning point for the local communities. By working together to protect their shared natural heritage, the chiefdoms have set an example of sustainable land management and conservation practices in Eswatini. This collaborative approach not only safeguards the forest’s biodiversity but also fosters a sense of unity and stewardship among the communities.